Here is a list of things we have.
- High Pressure Chamber
usually used for HIP (Hot Isostatic Pressing)
A chamber connected to a 3-stage compressor, working with gas (usually argon)
max pressure: ~1.5 GPa
inner diameter: 30 mm
inner lenght : ~30 cm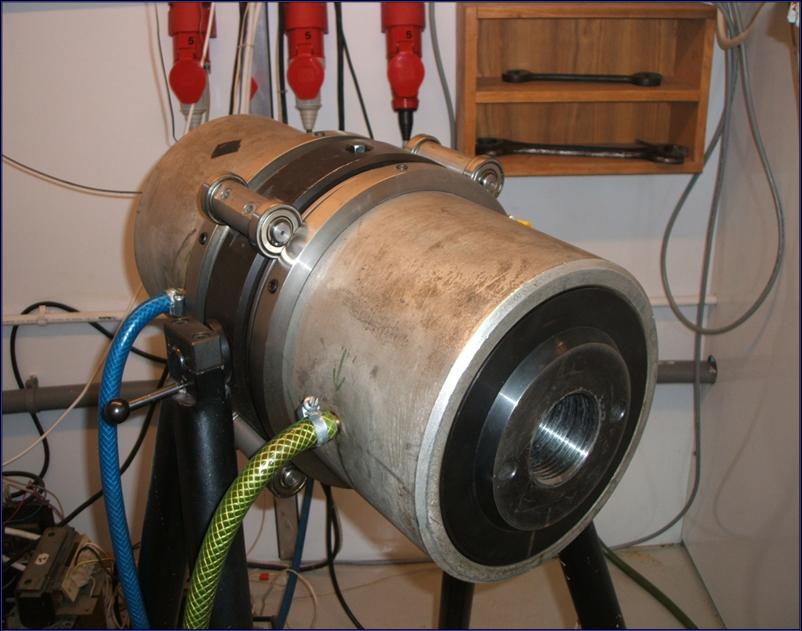
It is possible to insert a furnace in the chamber. Automatic T control.
max temperature: ~1100 C
inner diameter: 10-15 mm
inner lenght: ~15 cm
- - Single-axis Press
usually used for HP (Hot Pressing)
A hydraulic press using pressure from gas cylinder (usually with argon) with pressure stabilization, independent of sample shortening.
max press: ~65 tonnes
can be equiped with a furnace with a linear gas flow (e.g. argon). Automatic T control.
max temperature: ~800 C
- - 3-axial Mill
used for MA (Mechanical Alloying)
2 containers rotating symultaniously, filled with balls and milled material
materials for balls: steel, volfram, ZrO2
material for container inner walls: steel, ZrO2
3 independent engines, each with frequency control
- - Wire drawer
Equiped with a set of drawing dies. Adjustable
diameter range: 4.5 - 0.22 mm
drawing speed: ca. from 1 mm/s to 3 cm/s
reduction step: ~5%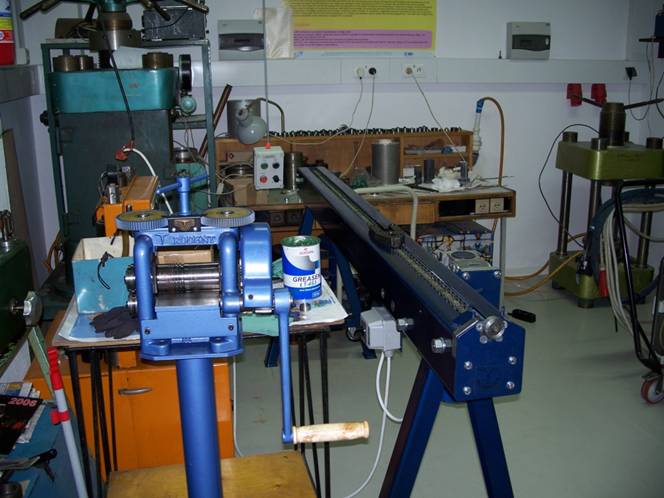
the roller (left) and the drawer (right)
- - Wire Roller
Used to roll tapes and to prepare wire endings before drawing
- - SHS Microwave Equipment
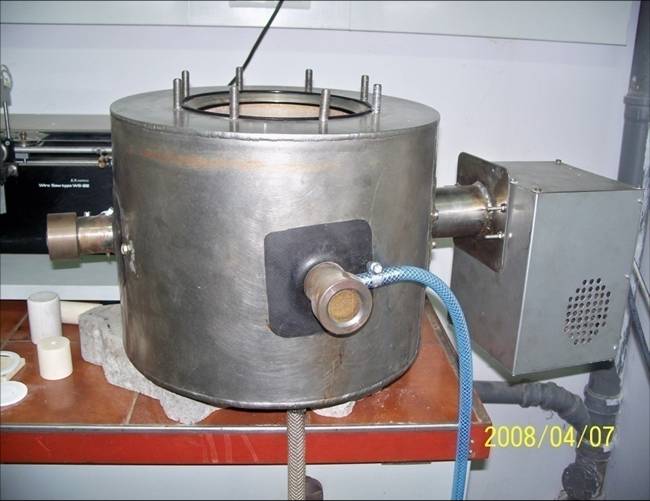

This process allows the synthesis of MgB 2 material in in situ material before it is placed in a
wire/container and subjected to final sintering. Presented equipment uses microwave generator as a source of heat that ignites the in situ sample, in protective, near-vacuum atmosphere. Ignition started inside the samples spreads outwards creating a shock wave that takes away major part of impurities from sample. After such rapid reaction only part of the material is reacted to MgB 2 and it can be still treated as an in situ precursor. Small grains of MgB 2 present in sample block growth of grains during final heat treatment.
- - High Pressure Ultrasonic Mixing and Purefying Equipment
Main idea behind this technique is to use argon gas under high pressure as a medium for spreading of ultrasonic waves. Argon density in room temperature at 1kbar is similar to density of water in normal conditions. Energetic ultrasonic waves penetrating the powder are able to efficiently grind its grains in a safe non-reactive argon atmosphere. Afterward, argon is deflated from the system through a filter that absorbs powder from gas. Moreover, large fraction of impurities that dwelled on surface of powder grains is striped and removed with gas. Additional filter is placed outside the chamber to absorb smaller grains of powder.
It is also possible to heat the sample up to 400 oC during process. This allows using other compounds, like MgH 2 that decompose from high temperature, producing highly reactive atomic magnesium, that easily reacts with boron, if it is present. For purification effectiveness helium is also used with argon, as it better penetrates between powder grains.
-